Category: aspiecoder.com
-
Strategies for Addressing Resistance to Change
To address resistance to new coding standards, experts recommend clearly communicating benefits, involving the team early, and gradually implementing changes. Key strategies include documenting advantages, fostering collaboration, using automated tools, providing support through pair programming, and handling concerns constructively while sharing success stories to build momentum and acceptance.
-

My Key Ingredients for Success as a Software Engineer: Mindfulness, Empathy, and Gratitude
The content emphasizes that alongside technical skills, personal qualities like mindfulness, empathy, and gratitude are essential for success in software engineering. Mindfulness helps in decision-making and stress management, empathy fosters effective collaboration and understanding user needs, while gratitude promotes a positive work environment and encourages growth.
-

The S in the SOLID Principal
The Single Responsibility Principle (SRP) posits that a class should have one defined responsibility, reducing complexity and enhancing modularity. Introduced by Robert C. Martin, SRP aids in crafting clearer, testable, and maintainable code by isolating functionalities. Violations lead to issues like “God Classes” and “Shotgun Surgery,” highlighting the need for focused design.
-

The History of Time-Sharing in Computing and the Evolution of Code Optimization
The history of time-sharing in computing highlights significant advancements and economic considerations. Originating in the late 1950s, it enabled simultaneous computer access for multiple users, necessitating highly optimized code. Although optimization declined with improved hardware, the rise of cloud computing has renewed this focus, aiming for efficiency and cost-effectiveness in resource utilization.
-
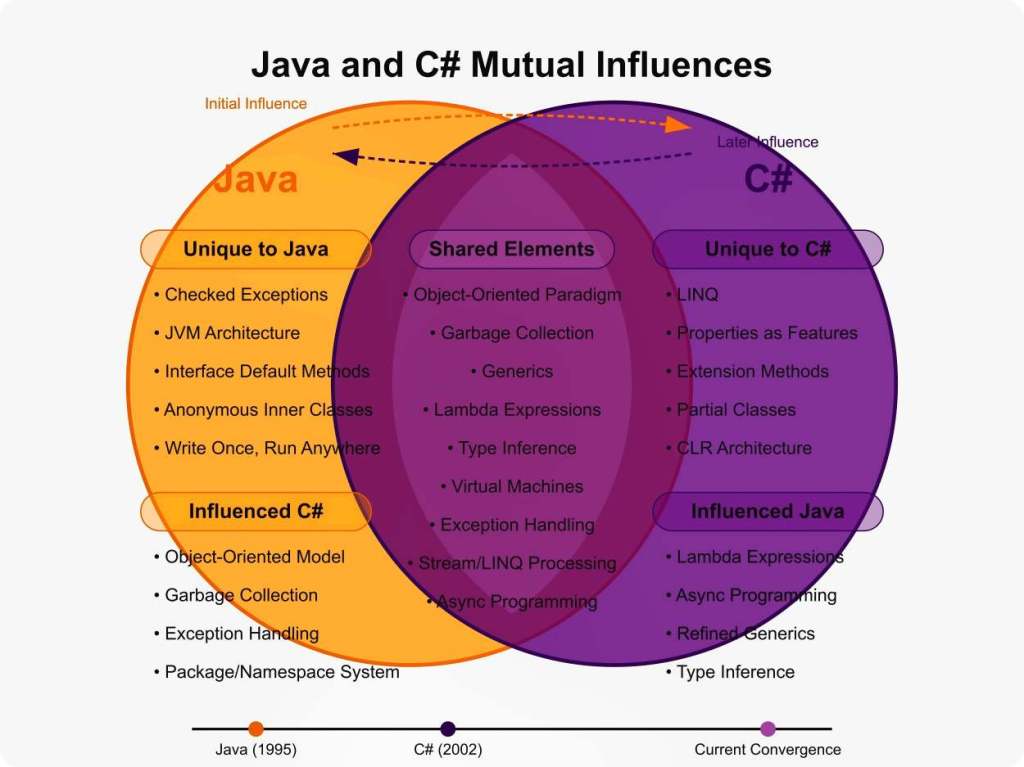
Technical Comparison of Java and C#: Mutual Influences
Java and C# are influential programming languages that have shaped each other through reciprocal borrowing of features and design principles. This document explores their evolution, technical traits, and parallel advancements, highlighting how concepts like object-oriented programming, generics, and functional programming have developed and converged, benefiting developers across both ecosystems.
-

The Tension Between Tooling and Management in Software Engineering: A Productivity Paradox
Over the past 40 years, software engineering has evolved through advanced tools and methodologies. Despite significant productivity gains from modern tools, software delivery often lags due to management complexities and process overhead. Balancing tooling with streamlined management practices is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving timely delivery in software development.
-

Null Values in Programming Languages: Concepts, History, Initial Languages, Pros, Cons, and Modern Impact
Null values are essential in programming, indicating the absence of valid data. While simplifying tasks like memory management, they can lead to significant errors, termed the “billion-dollar mistake” by Tony Hoare. This analysis explores null’s origins, advantages, disadvantages, and influence on modern programming practices, highlighting the shift towards safer coding paradigms.
-

The Role of Compilers, Interpreters, and JIT Environments in Software Engineering and Programming Language Theory
Compilers, interpreters, and JIT environments are crucial in software development, connecting human-readable code to machine execution. Compilers translate code ahead-of-time, interpreters execute it line-by-line for immediacy, and JIT compiles during runtime for optimization. Each tool influences performance, development speed, and adaptability, shaping programming language theory and software engineering practices.
-
From Atari to Micro SD: A Personal Journey Through Storage Density and Software Evolution
From the moment I unboxed my Atari 2600 in 1978 to the day I inserted a 256GB micro SD card into my Nintendo Switch, I have observed a significant evolution in storage density that has fundamentally transformed the field of software engineering. What began with the 2KB limitations of *Breakout* has evolved into an era…
-

The Hacker Ethic and Its Influence on Generation X Software Engineers
We owe a considerable debt of gratitude to the innovators of the late 20th century, particularly the Generation X cohort who matured alongside the rise of personal computing. This essay explores the significant and enduring impact of the “hacker ethic”—a set of principles that prioritize open access, information sharing, and an unwavering quest for knowledge—on…