Tag: c
-

The Paradox of “Less is More” in Software Engineering: When More Code Yields Better Performance
In software engineering, concise code is often preferable, but performance-critical scenarios may require more complex algorithms. This analysis compares Bubble Sort and QuickSort, highlighting how QuickSort’s additional code results in significantly better efficiency. Ultimately, balancing simplicity and performance is vital, depending on the application’s needs and data size.
-

What Beautiful Code Means: An Autistic Software Engineer’s Perspective
The concept of “beautiful code” for an autistic software engineer emphasizes clarity, elegance, maintainability, and efficiency. It promotes cognitive accessibility, enhances collaboration, and offers personal fulfillment. Beautiful code not only serves functional purposes but also creates sensory and emotional harmony, reflecting a deeper connection between logic and creativity in programming.
-
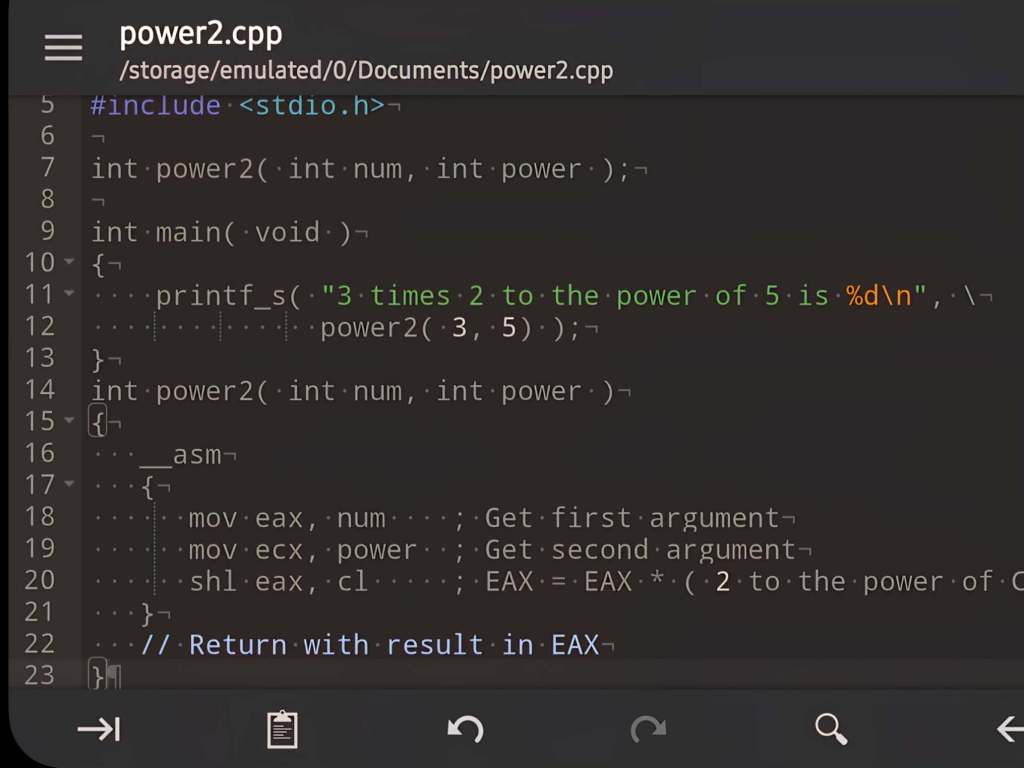
Software Compilers with Integrated Assembly Support: A Comprehensive Overview
Software compilers convert high-level programming languages into machine code, with integrated assembly enhancing developer control over hardware. This feature enables blending low-level efficiency with high-level productivity. The document reviews compiler history, mechanisms, application cases, and examples, emphasizing its significance in system programming, embedded systems, and performance optimization.
-

The Relationship Between CPU Design and Programming Language Theory Over the Past 50 Years
The essay explores the dynamic interplay between CPU design and programming language theory over fifty years. It traces developments from the 1970s to present, highlighting milestones such as structured programming with C, RISC architectures, and multicore processors. This evolving relationship has continuously influenced software optimization and hardware advancements, fostering innovation.
-
Determining Odd or Even Integers in C# Without Using the Modulo Operator
In C#, determining if an integer is odd or even can be done without the modulo operator. Three methods are explored: bitwise AND (fastest, suitable for performance), division and multiplication (most readable), and bitwise shift (less intuitive). Each method has advantages and disadvantages, influencing choice based on performance, readability, or complexity.
-
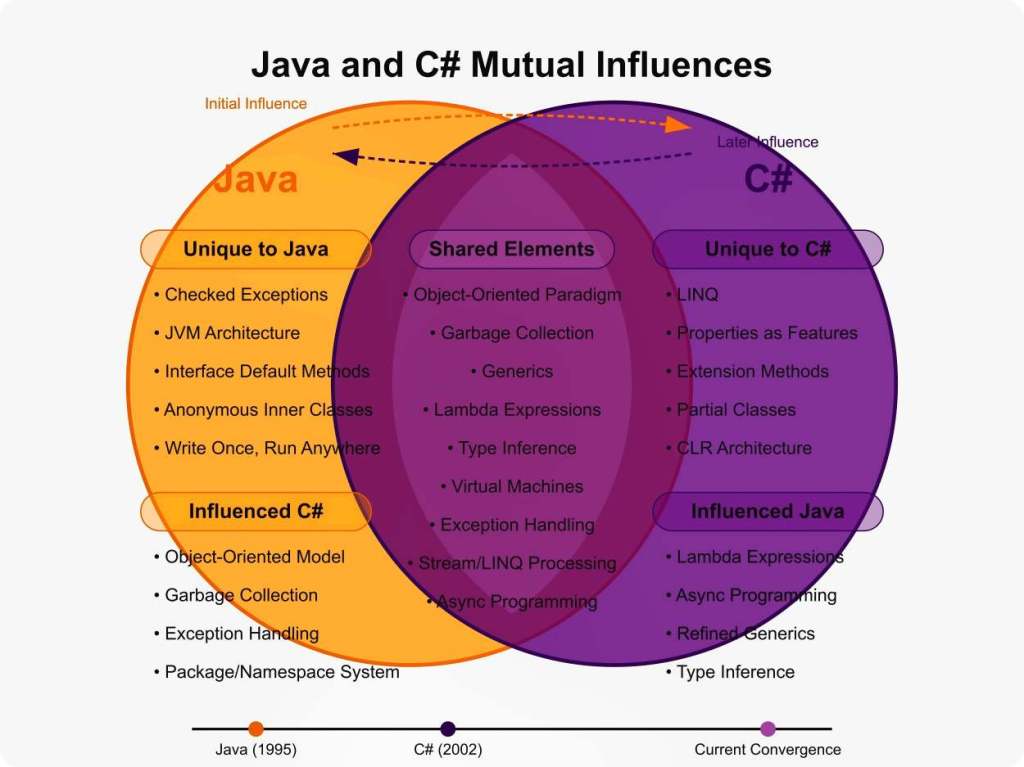
Technical Comparison of Java and C#: Mutual Influences
Java and C# are influential programming languages that have shaped each other through reciprocal borrowing of features and design principles. This document explores their evolution, technical traits, and parallel advancements, highlighting how concepts like object-oriented programming, generics, and functional programming have developed and converged, benefiting developers across both ecosystems.
-

Null Values in Programming Languages: Concepts, History, Initial Languages, Pros, Cons, and Modern Impact
Null values are essential in programming, indicating the absence of valid data. While simplifying tasks like memory management, they can lead to significant errors, termed the “billion-dollar mistake” by Tony Hoare. This analysis explores null’s origins, advantages, disadvantages, and influence on modern programming practices, highlighting the shift towards safer coding paradigms.
-

The Role of Compilers, Interpreters, and JIT Environments in Software Engineering and Programming Language Theory
Compilers, interpreters, and JIT environments are crucial in software development, connecting human-readable code to machine execution. Compilers translate code ahead-of-time, interpreters execute it line-by-line for immediacy, and JIT compiles during runtime for optimization. Each tool influences performance, development speed, and adaptability, shaping programming language theory and software engineering practices.
-

Conway’s Game of Life: From Mathematical Curiosity to Software Engineering Paradigm
In 1970, John Horton Conway introduced the Game of Life, a cellular automaton exhibiting complex behaviors from simple rules. The game significantly influenced software engineering by exemplifying declarative programming, emergence, and parallel processing. Its cultural impact spans multiple disciplines, continuing to inspire exploration and innovation in computing decades later.
-

Using LINQ and C# to Evaluate Yahtzee Dice Throws
When game logic intersects with contemporary programming paradigms, remarkable results can be achieved. This essay examines how C#’s LINQ features can effectively address the challenge of evaluating Yahtzee dice throws. By converting intricate pattern recognition and scoring rules into organized, functional code, we will illustrate how LINQ’s declarative style enhances clarity, which may otherwise be…